In the Spring Data JPA Example
we have already seen an integrated example of Spring MVC + JPA (Hibernate) + MySQL. In that example, query look up strategy
for user defined query was automatic where Spring framework did the work of deriving query by parsing the method name.
Though getting a query derived from the method name is quite convenient but you may face the situation where method
name parser does not support the keyword you used or the method name would get unnecessarily ugly. In that case you
can use JPA named queries using @NamedQuery annotation or annotate your query method with @Query.
In this article we'll see Spring data JPA example with @NamedQuery annotation.
For Spring Data JPA example using Query annotation check this post- @Spring Data JPA @Query Annotation Example
Spring Data JPA with named query
we’ll create a rest web service using Spring Web MVC, JPA implementation used is Hibernate and DB is MySQL.
Example shows the use of the <named-query /> element (in case of XML configuration) and @NamedQuery annotation. The queries for these configuration elements have to be defined in the JPA query language. If you want to define queries in native SQL you can use <named-native-query /> or @NamedNativeQuery too. But drawback with native SQL is that you lose the database platform independence.
Maven dependencies
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.knpcode</groupId> <artifactId>SpringJPAProject</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>war</packaging> <name>SpringJPA</name> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <spring.version>5.1.8.RELEASE</spring.version> <spring.data>2.1.10.RELEASE</spring.data> <hibernate.jpa>5.4.3.Final</hibernate.jpa> <mysql.version>8.0.17</mysql.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-core</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-web</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <!-- Spring data JPA --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId> <artifactId>spring-data-jpa</artifactId> <version>${spring.data}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId> <version>2.9.6</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId> <version>4.0.0</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <!-- Hibernate --> <dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-entitymanager</artifactId> <version>${hibernate.jpa}</version> </dependency> <!-- MySQL Driver --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>${mysql.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId> <version>1.7.25</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <sourceDirectory>src</sourceDirectory> <plugins> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.8.0</version> <configuration> <release>11</release> </configuration> </plugin> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.2.1</version> <configuration> <warSourceDirectory>WebContent</warSourceDirectory> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
Dependencies are added for Spring core, Spring context as well as for Spring Web and Spring data JPA.
Dependency for Hibernate is added as Hibernate JPA implementation is used.
MySQL connector is used for connecting to MySQL DB from Java application.
Jackson databind is needed for webservice responses which are sent as JSON.
DB table Query
MySQL DB table used for this Spring data JPA can be created using the following query.
CREATE TABLE `emp` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `first_name` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL, `last_name` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL, `department` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
JPA Entity – Spring data JPA
import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.GenerationType; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.NamedQuery; import javax.persistence.Table; @Entity @Table(name="emp") @NamedQuery(name = "Employee.findByDepartment", query = "select e from Employee e where e.dept = ?1") public class Employee { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private int id; @Column(name="first_name") private String firstName; @Column(name="last_name") private String lastName; @Column(name="department") private String dept; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getFirstName() { return firstName; } public void setFirstName(String firstName) { this.firstName = firstName; } public String getLastName() { return lastName; } public void setLastName(String lastName) { this.lastName = lastName; } public String getDept() { return dept; } public void setDept(String dept) { this.dept = dept; } @Override public String toString() { return "Id= " + getId() + " First Name= " + getFirstName() + " Last Name= " + getLastName() + " Dept= "+ getDept(); } }
This is the entity class which corresponds to the emp table in DB.
@Entity annotation specifies that this model class is an entity.
@Table annotation specifies the primary table for the entity.
@NamedQuery annotation specifies the named query. If you have more than one query you can use @NamedQueries annotation. For example-
@NamedQueries({ @NamedQuery(name = "Employee.findByDepartment", query = "Select e from emp e where e.department = ?1"), @NamedQuery(name="Employee.findByLastName", query = "Select e from emp e where e.lastName = ?1""), })
@Id annotation specifies the primary key of the entity.
@GeneratedValue specifies the primary key generation strategy which is autoincrement in this case.
@Column annotation specifies the mapped table column name for the field.
In case of XML configuration <named-query /> element is used for defining named query.
<named-query name="Employee.findByDepartment"> <query>Select e from emp e where e.department = ?1</query> </named-query>
Spring Data JPA Repository
import java.util.List; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; import com.knpcode.springproject.model.Employee; public interface EmployeeRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Integer> { List<Employee> findByLastName(String lastName); List<Employee> findByDepartment(String department); }
EmployeeRepository interface extends JpaRepository which takes the domain class to manage (Employee in this case) as well as the id type of the domain class as type arguments.
Apart from the methods inherited from JPARepository there are two methods defined in EmployeeRepository inerface.
Spring Data tries to resolve a call to these methods to a named query, starting with the simple name of the configured domain class, followed by the method name separated by a dot. So, for the method findByDepartment named query (Employee.findByDepartment) is used whereas for findByLastName Spring data creates a query from the method name.
Spring Data JPA example – Service class
From the service layer we’ll call the repository methods. Notice that repository instance has to be injected in the service class.
import java.util.List; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import com.knpcode.springproject.dao.EmployeeRepository; import com.knpcode.springproject.model.Employee; @Service public class EmployeeService { @Autowired private EmployeeRepository repository; public Employee getEmployeeById(int id) { return repository.findById(id).get(); } public List<Employee> getAllEmployees(){ return (List<Employee>) repository.findAll(); } public void deleteEmployeeById(int id){ repository.deleteById(id); } public Employee addEmployee(Employee emp) { return repository.save(emp); } public List<Employee> getEmployeeByLastName(String lastName) { return repository.findByLastName(lastName); } public List<Employee> getEmployeeByDepartment(String department) { return repository.findByDepartment(department); } }
Rest Controller
Using a Rest controller class we’ll map the path to the methods that are to be called for the requests.
import java.util.List; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import com.knpcode.springproject.model.Employee; import com.knpcode.springproject.service.EmployeeService; @RestController @RequestMapping("/employee") public class EmployeeController { @Autowired EmployeeService empService; @GetMapping("/{id}") public Employee getEmployeeById(@PathVariable int id) { return empService.getEmployeeById(id); } @GetMapping public List<Employee> getAllEmployees(){ return empService.getAllEmployees(); } @DeleteMapping("/{id}") @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK) public void deleteEmployeeById(@PathVariable int id){ empService.deleteEmployeeById(id); } @PostMapping @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED) public Employee addEmployee(@RequestBody Employee emp) { return empService.addEmployee(emp); } @GetMapping("/lastname/{lastName}") public List<Employee> getEmployeeByLastName(@PathVariable String lastName) { return empService.getEmployeeByLastName(lastName); } @GetMapping("/dept/{department}") public List<Employee> getEmployeeByDepartment(@PathVariable String department) { return empService.getEmployeeByDepartment(department); } }
Spring Data JPA – configuration classes
In this Spring data JPA example Java configuration is used so class is annotated with @Configuration annotation.
For setting up DataSource DB properties are read from a properties file, path for the properties file is configured using @PropertySource annotation.
@EnableJpaRepositories annotation enables the JPA repositories. Package to scan for the repositories is provided as a value with this annotation.
@EnableTransactionManagement annotation enables Spring's annotation-driven transaction management capability.
With in this Java config class we set up a EntityManagerFactory and use Hibernate as persistence provider.
import java.util.Properties; import javax.sql.DataSource; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; import org.springframework.core.env.Environment; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories; import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource; import org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager; import org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean; import org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaVendorAdapter; import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement; @Configuration @EnableJpaRepositories("com.knpcode.springproject.dao") @EnableTransactionManagement @PropertySource("classpath:config/db.properties") public class JPAConfig { @Autowired private Environment env; @Bean public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactory() { HibernateJpaVendorAdapter vendorAdapter = new HibernateJpaVendorAdapter(); LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean factory = new LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean(); factory.setJpaVendorAdapter(vendorAdapter); factory.setPackagesToScan("com.knpcode.springproject.model"); factory.setDataSource(dataSource()); factory.setJpaProperties(hibernateProperties()); return factory; } @Bean public DataSource dataSource() { DriverManagerDataSource ds = new DriverManagerDataSource(); ds.setDriverClassName(env.getProperty("db.driverClassName")); ds.setUrl(env.getProperty("db.url")); ds.setUsername(env.getProperty("db.username")); ds.setPassword(env.getProperty("db.password")); return ds; } Properties hibernateProperties() { Properties properties = new Properties(); properties.setProperty("hibernate.dialect", env.getProperty("hibernate.sqldialect")); properties.setProperty("hibernate.show_sql", env.getProperty("hibernate.showsql")); return properties; } @Bean public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager() { JpaTransactionManager txManager = new JpaTransactionManager(); txManager.setEntityManagerFactory(entityManagerFactory().getObject()); return txManager; } }
If you are using XML configuration then the configuration for enabling JPA repositories is-
<jpa:repositories base-package="com.knpcode.springproject.dao"/>db.properties file
db.driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver db.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/knpcode db.username= db.password= hibernate.sqldialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect hibernate.showsql=true
To set up the web application using Java config rather than using the web.xml we’ll need the following classes.
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer; public class WebConfigInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer { @Override protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() { return new Class<?>[] {WebConfig.class}; } @Override protected String[] getServletMappings() { return new String[] {"/"}; } }
@Configuration @EnableWebMvc @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.knpcode.springproject") public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer{ }
Deploying the Spring Data JPA application
Right clicking the project and select Run As – Maven build, provide goal as clean install. If the build is successful you will have your application packaged as a war which you can deploy on web container like Tomcat and then test the application.
For testing the RESTful webservice, Postman rest client is used.
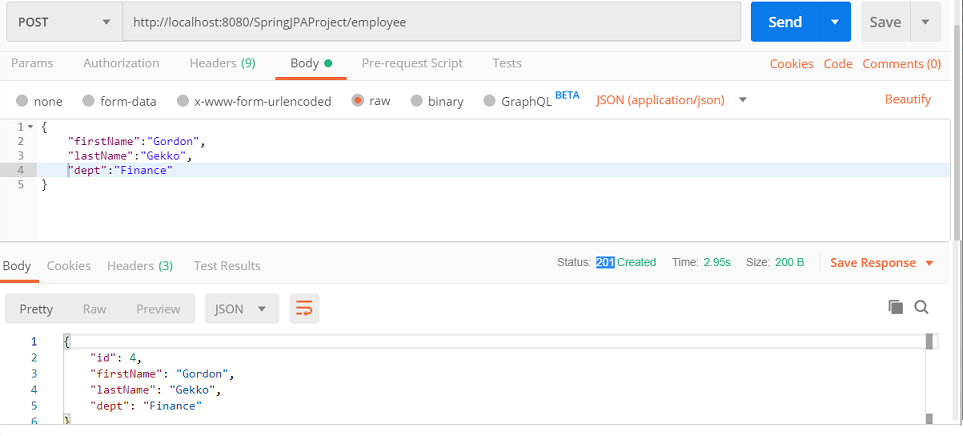
Adding employee
Note that the request selected is POST and the URL is http://localhost:8080/SpringJPAProject/employee
Data is sent as request body in JSON format. In the response added Employee data is sent back.
Find by departement (named Query)
You can also also send requests directly from browser as done for this request.
Get Employee by last name
That's all for the topic Spring Data JPA @NamedQuery Annotation Example. If something is missing or you have something to share about the topic please write a comment.
You may also like


No comments:
Post a Comment