In this articles we’ll go through some of the basics of Spring Data REST and see an example of using Spring Boot with Spring Data REST.
Spring Data REST
Spring Data REST builds on top of the Spring Data repositories and automatically exports those as REST endpoints. It takes the features of Spring HATEOAS and Spring Data and automatically combines them together.
In the Spring Boot + Spring Data JPA + MySQL + Spring RESTful example you can see how using Spring Data JPA requires that you just create a Repository interface. No need to write DAO implementation classes Spring takes care of automatically implementing this repository interface.
Spring Data REST goes one step further, you don’t even need to create a Controller class with mappings (GET, POST, PUT etc.). By using the domain class used with in the Repository interface Data REST automatically exposes the methods provided by Spring Data JPA as REST end points. Let’s see it in action with the help of an example.
Maven Dependencies
In the pom.xml file add the following starter dependencies.
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-rest</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <!-- MySQL Driver --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> </dependencies>
This example uses MySQL DB as backend so driver for that is added.
DB table Query
MySQL DB table used for this Spring Boot and Spring data REST example can be created using the following query.
CREATE TABLE `employee` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `first_name` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL, `last_name` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL, `department` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
Domain class (Entity class)
Entity class which maps to the employee table in DB.
import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.GenerationType; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.Table; @Entity @Table(name="employee") public class Employee { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private int id; @Column(name="first_name") private String firstName; @Column(name="last_name") private String lastName; @Column(name="department") private String dept; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getFirstName() { return firstName; } public void setFirstName(String firstName) { this.firstName = firstName; } public String getLastName() { return lastName; } public void setLastName(String lastName) { this.lastName = lastName; } public String getDept() { return dept; } public void setDept(String dept) { this.dept = dept; } @Override public String toString() { return "Id= " + getId() + " First Name= " + getFirstName() + " Last Name= " + getLastName() + " Dept= "+ getDept(); } }
Data JPA Repository Class (Employee Repository)
import java.util.List; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; import org.springframework.data.repository.query.Param; import com.knpcode.model.Employee; public interface EmployeeRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Integer> { List<Employee> findByLastName(@Param("name") String lastName); }
This repository is an interface that lets you perform various operations involving Employee objects. It gets these operations by extending the JPARepository interface that is defined in Spring Data Commons.
At runtime, Spring Data REST automatically creates an implementation of this interface.
For this EmployeeRepository interface, Spring Data REST exposes a collection resource at "/employees" by default. This path is derived from the uncapitalized, pluralized, simple class name of the domain class being managed. It also exposes an item resource for each of the items managed by the repository under the URI template "/employees/{id}".
DB Configuration
By default Spring boot reads properties file at this location src/main/resources/application.properties. You must define the DB connection attributes and Hibernate related properties in the application.properties file.
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/knpcode spring.datasource.username=admin spring.datasource.password=password spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.sqldialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLInnoDBDialect spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.showsql=true
Create Spring Boot Application Class
Here is an application class with the main method which is the entry point for Spring Boot application.
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication public class DataRestApp { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(DataRestApp.class, args); } }
That’s all you need to have a fully functional REST API. Run it as a stand alone Java application by running the class with the main method (DataRestApp.java) from Eclipse IDE itself.
Right click DataRestApp.java – Run As – Java Application
To discover what resources are available at the root of the application, issue an HTTP GET to the root URL (http://localhost:8080/)
As you can see “/employees” endpoint is available to get all the employees. There are also ?page,size,sort options available.
A profile endpoint “/profile”, is a place to include application-level details.
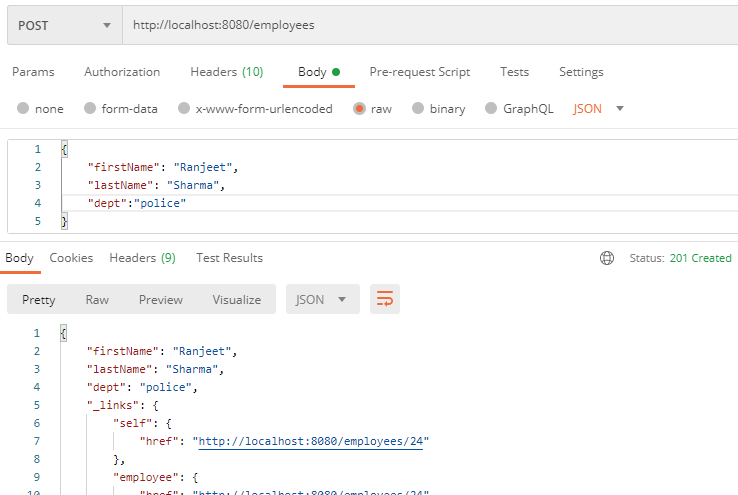
Adding an Employee-
Using Postman client you can send a POST request to add employee record.
If you look at the response headers in the Postman client, you will notice that the content-type is 'application/hal+JSON'
By default, Spring Data REST uses HAL to render responses. Hypertext Application Language (HAL) is a simple language that gives a consistent and easy way to hyperlink between resources in API.
Getting all employees-
Getting employee by ID-
Using @RepositoryRestResource to customize REST endpoints
If you want to change this default path you can use @RepositoryRestResource annotation to do that. Both the name of the resource and the path can be customized by using @RepositoryRestResource on the repository interface.
import java.util.List; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; import org.springframework.data.repository.query.Param; import org.springframework.data.rest.core.annotation.RepositoryRestResource; import com.knpcode.model.Employee; @RepositoryRestResource(collectionResourceRel = "employee", path = "employee") public interface EmployeeRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Integer> { List<Employee> findByLastName(@Param("name") String lastName); }
With this change you can get the list of all employees by using the following URL.
http://localhost:8080/employee
For getting employee detail by ID-
http://localhost:8080/employee/23
You can also issue PUT, PATCH, and DELETE REST calls to replace, update, or delete existing records respectively. The following example uses a PATCH call to update a subset of items.
Changing the Base URI
By default, Spring Data REST serves up REST resources at the root URI, '/'. You can change the base URI by setting a single property in application.properties, as follows:
spring.data.rest.basePath=/app
Now you can use the following URL to access all employees.
http://localhost:8080/app/employee
Accessing Data JPA custom query
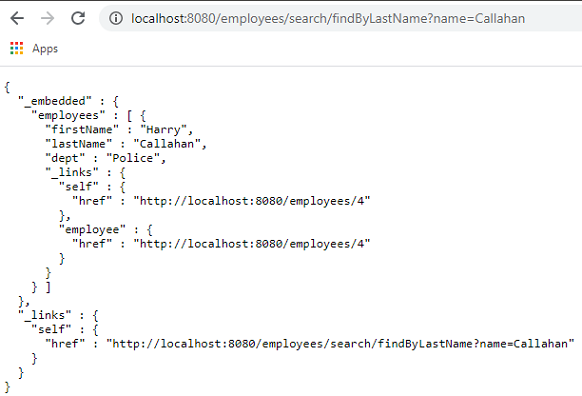
In the EmployeeRepository interface there is a custom method findByLastName(). You can find all query methods exposed by a repository by using search resource which returns links for all query methods.
You can see the URL for the query which by default matches the custom method name. The HTTP query parameter, name, matches the @Param("name") annotation used in the method in repository interface.
Using @RestResource annotation to change query method path
To change the segment of the URL under which this query method is exposed, you can use the @RestResource annotation as the following example shows.
public interface EmployeeRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Integer> { @RestResource(path = "lastname") List<Employee> findByLastName(@Param("name") String lastName); }
Then you can use following URL to access query method.
http://localhost:8080/employees/search/lastname?name=Callahan
That's all for the topic Spring Boot + Spring Data REST Example. If something is missing or you have something to share about the topic please write a comment.
You may also like
- Spring Boot + Data JPA + Oracle One to Many Example
- Spring Data JPA @Query Annotation Example
- Spring Boot Properties File: @ConfigurationProperties Example
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Autowiring in Spring
- Spring Bean Scopes
- How to Synchronize Java ArrayList
- Java Generics- Generic Class, Interface And Method
- Tic-Tac-Toe Game in Python
- Shuffle Phase in Hadoop MapReduce
- React useState Hook With Examples





No comments:
Post a Comment